Hyperbola
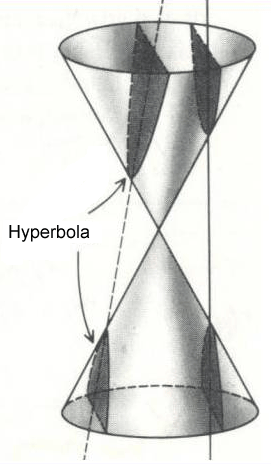
If the plane cuts through both nappes of the cone, the curve is called a hyperbola.
A hyperbola is the set of points P(x, y) in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between the distances from P to two fixed points in the plane, F1 and F2, called the foci, is a constant.
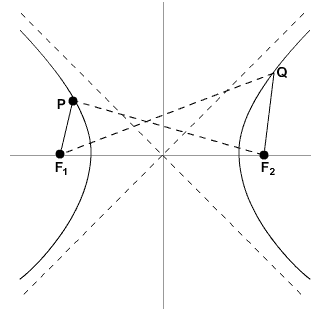
The hyperbola has two axes of symmetry. One axis contains the transverse axis and the other contains the conjugate axis.
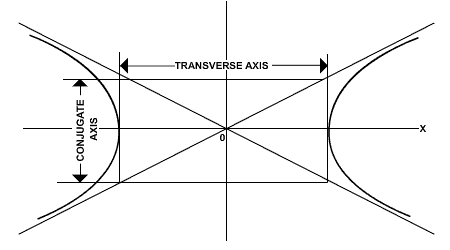
In the image above, "a" is defined as the distance from the center to the endpoint of the transverse axis; "b" is the distance from the center to the endpoint of the conjugate axis.
The standard equation of a hyperbola falls into the following two categories.
Horizontal Transverse Axis
Vertical Transverse Axis