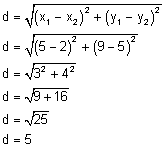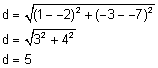Examples
Example 1: Given A(5, 9) and B(2, 5), we find the distance between A and B or the length of AB as follows:
x1 = 5 and x2 = 2
y1 = 9 and y2 = 5
Then
Example 2: Find the distance of CD if C (1,-3) and D (-2,-7).
As you can see, AB = CD, even though they have different endpoints.