Function Notation
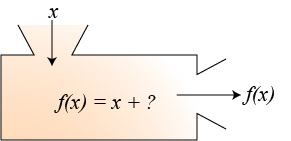
Function Machine
Functions come with their own notation that helps us work with linear and quadratic functions. This notation is written as f(x) and is read "f of x". You can think of f(x) as equal to y, or y = f(x). You can also think of the ordered pairs (x, y) as equal to (x, f(x)).
We can rewrite the linear function y = 2x – 8 as f(x) = 2x – 8.
Imagine the function as being a big machine. You feed the machine an x-value and the machine spits out an f(x) value.
Let’s take a look at our function f(x) = 2x - 8. Imagine that you feed the function a value of x = 4. What value of f(x) does the machine spit out?
f(x) = 2x – 8
f(4) = 2(4) – 8
f(4) = 8 – 8
f(4) = 0
Visit the Shodor website and the Math Playground website to access games using the function machine. You can access other function machine activities on the Shodor website by searching with the words "Function Machine."
Now that you know function notation, you can write inverse functions using function notation. For example, find the inverse of f(x) = 4x – 2. Instead of interchanging x and y, you interchange x and f(x). The inverse is then written as f–1(x). It looks like f has an exponent of -1 but this is the notation for an inverse function. Therefore, the inverse of f(x) = 4x – 2 is 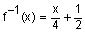 .
.
One final note. The function does not always have to be denoted as f(x). You can use letters other than f. You will most often see g(x) and h(x).