Barrier Methods
The barrier methods of contraception prevent the male sperm from meeting the female egg. Methods are outlined here.
Cervical Cap

- Made of latex rubber and fits over the cervix.
- Stops sperm from entering the uterus.
- Must be fitted by a medical professional.
- Offers no protection from STDs.
- Occasional mild allergic reactions to rubber or cream or jelly may occur.
- The cap may occasionally become dislodged during sex.
- Only three sizes are available and will not fit all women.
- May be used by women who cannot use the diaphragm.
Male Condoms

- A tube of latex or animal tissue placed onto a man's erect penis before intercourse.
- Collects a man's semen and keeps sperm from entering the other person's body.
- Offers some protection against STDs.
- The use of spermicidal foams, creams, and jelly increases this protection.
- A new condom must be used for each act of intercourse.
- Wearing one condom over another for added protection can tear the condom.
- Condoms may be purchased by men and women, and there are no age restrictions.
- After ejaculation, but before losing the erection, the rim of the condom must be held against the penis as the man withdraws to prevent the condom from slipping and spilling semen.
The Female Condom

- A large pouch made of thin plastic inserted into the vagina, lining the cervix and vagina, and covering the area around the vaginal opening.
- Stops semen from entering a woman's vagina.
- Must not be used with the male condom—can rupture either or both and become ineffective.
- Offers some protection from STDs.
- It should be taken out after intercourse and a new one used prior to each intercourse.
Diaphragm
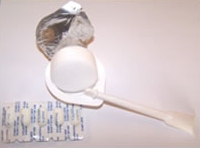
- A soft rubber cup with a flexible rim around the edge inserted next to the cervix before intercourse, covering the entrance to the uterus.
- It should always be used with a spermicide.
- It must be fitted by a medical professional and fit properly in order to work well.
- A diaphragm may become dislodged during sex.
- Need to check for holes in rubber dome occasionally.
- Must be removed within 24 hours; there is a possibility of toxic shock.
- May cause frequent bladder infections.