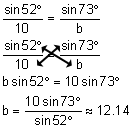The Law of Sines
|
The Law of Sines states that in any triangle the sine of an angle and its opposite side is proportional to the sine of any other angle and its opposite side. If the side lengths are a, b, and c and the opposite angles are A, B and C, respectively, then: |
Let’s look at how that works.
Example:
Find the length of b.
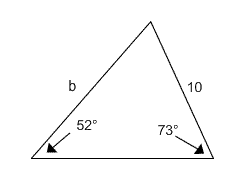 |
Triangle with Two Angles and a Non-Included Side |
First of all, note that we are given two angles and a non-included side. This is one of the situations that can be applied to the Law of Sines.
![]()
a = 10
![]()
b = ?