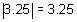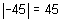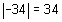Absolute Value
|
Definition of Absolute Value The absolute value of a real number is the distance it is from the origin, or zero, on the number line. |
The numbers 3 and –3 are two distinct, different numbers. As you can see on the number line below, both numbers are three units from zero. Therefore, they both have the same absolute value, that being 3.
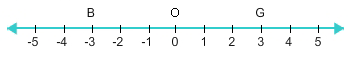
Since OB = OG, the numbers corresponding to B and G, that being -3 and 3 respectively, have the same absolute value.
The absolute value of any real number is the positive value of that number or the distance from that number on the number line to zero. It is important to remember that absolute values are always positive.
For example, the absolute values of -3.2, -2.67, -4, 4, 11.26, and 34 are 3.2, 2.67, 4, 4, 11.26, and 34, respectively. The absolute value of a number is denoted by placing the number between two short vertical lines, ![]() .
.
For example,