Water Erosion

Have you ever seen a movie where someone gets shrunk to the size of a bug? In their tiny form, just making it across the lawn is a daunting task. The blades of grass are like giant trees making a dense impenetrable forest, and a single drop of rain is a crushing flood that knocks them down and sweeps them away. A particle of soil, even much smaller than a bug, fares even worse under the impact of falling rain. A drop of rain falls at about 20 miles per hour. Upon impact with the ground, the rain breaks apart clumps of soil into individual particles that are then easily blown away by wind or carried away by rainwater.
Because soil is so important, the loss, erosion, or degradation of soil is of special environmental concern. Running water (like rainwater) is the leading cause of erosion, since it can easily take soil with it as it flows downhill or moves across the land. If soil is left unprotected and vulnerable to this kind of erosion, it can be quickly washed away. You may have observed this in the warm-up activity when you compared how simulated rainfall affected bare versus covered soil. Click through the tabs to see some images of water erosion.
Rill Erosion

Rill erosion is a kind of water erosion that occurs when water begins to flow over land in small channels called rills, cutting away at the topsoil as it flows.
Gully Erosion

Rills grow larger over time and eventually form wide gullies. Gully erosion is a kind of water erosion that occurs when water cuts through soil to the point that a steep gully is formed.
Sheet Erosion

Sheet erosion is a kind of water erosion that occurs when large sheets of water flow over an area. This commonly happens after heavy rain. In this picture, the water carried lots of debris and soil along with it.
Glacial Erosion
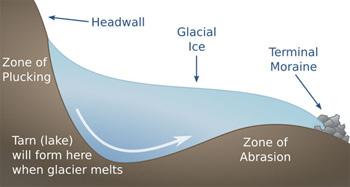
Because glaciers are made of frozen water, the erosion work they do is included with other forms of water erosion. Glaciers move over the land and drag soil with them, just as liquid water carries soil particles with it. Plucking is a specific kind of ice erosion in which glaciers cause large pieces of rock to break apart. The pieces are then transported by the glacier, by gravity, or by glacial melt water. In this picture, you see a zone of plucking where soil and rocks are moved by the glacier. They are then transported by the glacier to the terminal moraine zone, where they build up and accumulate.