The Natural Greenhouse Effect
Climate on earth is also kept stable by the greenhouse effect. Any changes to the normal functioning of the greenhouse effect can result in severe climate changes on the planet. The greenhouse effect is a natural warming of the earth’s atmosphere caused by heat-trapping gases that do not permit infrared radiation emitted from the earth’s surface to pass through the atmosphere and escape into space. The primary greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide and methane, but nitrous oxide and water vapor also play a part. Take a look at this avatar to refresh your memory of the greenhouse effect. Click the Avatar to listen to the explanation of the greenhouse effect.
![]() Avatar: The Greenhouse Effect
Avatar: The Greenhouse Effect
The version below has closed captions
Text Version
Human Activities and the Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gases are part of the global biogeochemical cycles and are necessary to maintain a stable temperature on the planet. However, human activities are increasing the production of greenhouses gases faster than at any other time in earth’s history. Browse through the galleria to find out how human activities alter the earth’s natural greenhouse effect.
Click each image below.
 The natural greenhouse effect has been altered by the global burning and use of fossil fuels. It is estimated that nearly 85% of our global energy needs are met by fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. Release of carbon dioxide from the use of fossil fuels contributes to the greenhouse effect.
The natural greenhouse effect has been altered by the global burning and use of fossil fuels. It is estimated that nearly 85% of our global energy needs are met by fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. Release of carbon dioxide from the use of fossil fuels contributes to the greenhouse effect.
 Extraction of oil and other fossil fuels releases carbon into the ocean and the atmosphere. This oil spill not only represents an ecological disaster for this area of the ocean, but also contributes to the greenhouse effect as excess carbon is added to the system.
Extraction of oil and other fossil fuels releases carbon into the ocean and the atmosphere. This oil spill not only represents an ecological disaster for this area of the ocean, but also contributes to the greenhouse effect as excess carbon is added to the system.
 Our reliance on transportation using these fossil fuels contributes a significant amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
Our reliance on transportation using these fossil fuels contributes a significant amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere.
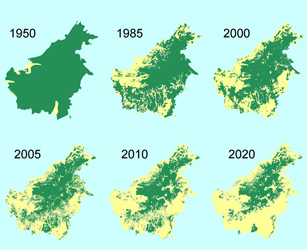 Deforestation can also contribute to the changes in the greenhouse gases. With less vegetation to recycle carbon dioxide in the process of photosynthesis, more carbon is left in the atmosphere. This map of Borneo shows the projected disappearance of the green forest from 1950 to 2020.
Deforestation can also contribute to the changes in the greenhouse gases. With less vegetation to recycle carbon dioxide in the process of photosynthesis, more carbon is left in the atmosphere. This map of Borneo shows the projected disappearance of the green forest from 1950 to 2020.
 The raising of livestock such as cows, sheep, buffalo and goats contributes to increased global methane levels. Methane, a greenhouse gas, has risen sharply since methane levels were first measured.
The raising of livestock such as cows, sheep, buffalo and goats contributes to increased global methane levels. Methane, a greenhouse gas, has risen sharply since methane levels were first measured.
 The waste collected at this landfill contributes to the atmospheric levels of methane as the garbage decomposes over time. Methane traps heat in the atmosphere much more effectively than carbon dioxide.
The waste collected at this landfill contributes to the atmospheric levels of methane as the garbage decomposes over time. Methane traps heat in the atmosphere much more effectively than carbon dioxide.
 Fertilizers used for crops, human and animal waste, and car exhaust contribute to rising nitrous oxide levels in the atmosphere.
Fertilizers used for crops, human and animal waste, and car exhaust contribute to rising nitrous oxide levels in the atmosphere.
 Fluorocarbons such as CFCs, which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators, trap heat in the atmosphere. CFCs are now banned in the US, helping to reduce this greenhouse gas.
Fluorocarbons such as CFCs, which are found in air conditioners and refrigerators, trap heat in the atmosphere. CFCs are now banned in the US, helping to reduce this greenhouse gas.
(image source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2008-07-11_Air_conditioners_at_UNC-CH.jpg)
Tutorial: Land and Climate
There are so many processes on the planet that maintain our climate. We already know that land absorbs and emits heat differently than water does, which has an impact on climate.
There are always ways in which the topography that we humans create affects climate. Think about how the topography of New York City is different today than it was before humans arrived. Do you think those skyscrapers have any effect on the local climate there? They sure do! Tall buildings, asphalt, concrete, and brick hold heat and block wind flow, which means that cities are generally warmer and have less air flow than surrounding areas. Less airflow often means more haze and smog. Yuck!
How does topography affect the earth’s climate? Let’s find out more in this tutorial.
Text Version
Climate Review
You’ve seen how many things influence and support the earth’s climate. Climate science is complex and evolving, and you’ll learn more about as the course continues. For now, let’s review your learning so far in this game.












