Viral STDs: Genital Warts, Herpes, AIDS (continued)
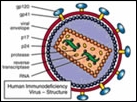
HIV/AIDS
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is contracted during unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who is infected with the virus. It can also be contracted by sharing needles to inject drugs, or through infected blood.
The symptoms for AIDS may show up several months to several years after initial contact with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. The disease itself may be present for many years with no actual symptoms. The following are symptoms that are a result of an HIV infection:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chronic tiredness
- Flu-like feelings that do not go away
- Chronic diarrhea
- Yeast infections (for women) that do not go away
There is no cure for HIV/AIDS. People who have HIV/AIDS take a "cocktail" of drugs to block the cells from producing the HIV. It can result in serious illness and death. A mother can pass this disease to her baby during childbirth or breastfeeding.
Self-check:
Abstinence is the only 100 percent sure way to avoid HIV/AIDS. If a person decides to engage in sexual contact, he or she should limit sex to one trusted partner; use effective barrier contraception; talk with your partner; get tested and ask your partner to get tested before you have sex.