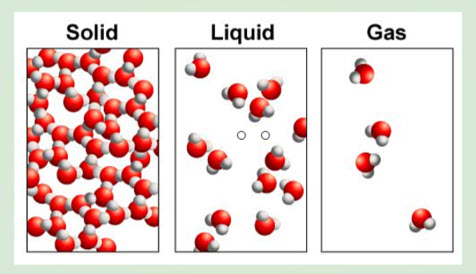
What's the Matter?
Take a look at your notebook right now. Draw a square on it that is roughly 2cm on each side. Now divide that into 10 sections. Take one of those 10 pieces and divide it into 10. Now take one of those 10 and divide it into 10. Getting harder? If we did this 6 more times, we'd have a piece of paper the size of an atom! That's small! To think of it a different way, it would take 100 million atoms lined up side by side to equal the width of the 2cm2 piece of paper you started with!
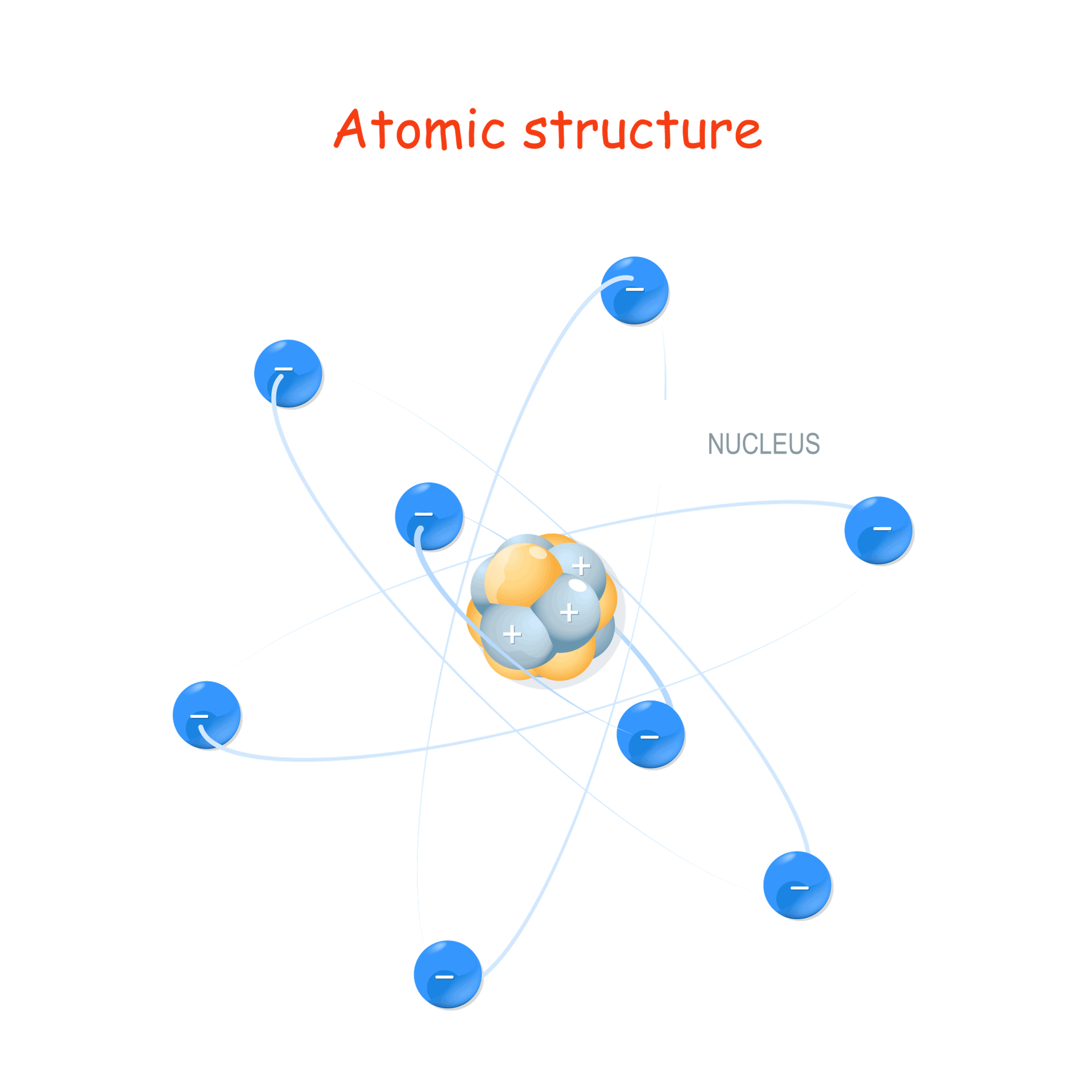
If we continued to divide that up, we'd get down to the size of even smaller subatomic particles that make up an atom: protons, neutrons, and electrons. All matter is made up of atoms and the subatomic particles that compose an atom
is made up of atoms and the subatomic particles that compose an atom .
.
Atoms combine to form...
Click each picture below.
- Elements
A fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means. Examples include sulfur, copper, gold, and silver.
- Compounds
Combinations of two or more elements held together in fixed proportions. Water is an example of a compound.
- Molecules
A combination of two or more atoms of different elements held together by chemical bonds. Carbon dioxide and methane gas are examples of molecules. Lipids like butter or plastics, which are polymers, are also examples.
 Webquest: The Periodic Table
Webquest: The Periodic Table
In the following webquest activity, you will be researching different forms of the periodic table to discover how it is organized. In addition, you will be learning about the atomic number, atomic mass and isotopes.
Download the Webquest: The Periodic Table worksheet to get started.
Matter Review
Step through the slideshow below.
-
The most well known theory proposed by John Dalton states that all matter is made of atoms and that they cannot be subdivided or destroyed by chemical means. In addition atoms with particular characteristics are called elements and can combine to form complex structures such as compounds.
-
A positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
-
A negatively charged subatomic particle found circulating around the outside of the nucleus of an atom.
-
This subatomic particle has no charge and is found in the nucleus along side the protons.
-
The periodic table is a list of all the known elements on earth. It is organized in increasing atomic number.
-
These are isotopes of hydrogen. Isotopes are different atoms of the same element having a different number of neutrons. The most common form of hydrogen has no neutrons, deuterium has one and tritium has two.
-
This is the ratio of elements that bind together. For instance H2O is the chemical formula for water. This means we have two hydrogen atoms for every one oxygen atom in this molecule.
-
Methane, CH4; is among the simplest organic compounds. One or more atoms of carbon are covalently bonded to atoms of other elements, most often hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
-
A chemical compound containing carbon and other elements. Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO)
Text Version
There is No "Away"
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. This is a scientific law the law of conservation of matter. So when we throw our trash away, recycle it or compost it, what happens to it? As you can see, there is no "away". Matter can be converted from one form to another, like oranges to soil, but atoms cannot be created or destroyed.



Kinetic and Potential Energy: Go for the Gold!
The universe is made up of more than just matter. Energy keeps us moving and fuels all the work we do. Athletes at the Olympics depend upon maximizing their energy to get that coveted gold medal. Take a look at the video "The Science of Snowboarding" to learn more about the ways in which snowboarders maximize their potential and kinetic energy.
Click the link to watch the YouTube Video: The Science of Snowboarding
Text Version
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is moving energy. Flying down the half pipe is an example of kinetic energy. Other types of kinetic energy include heat, which comes from the movement of atoms, molecules, or ions in a substance, and electromagnetic energy, which is light.
Potential Energy
Potential energy is stored energy. Think of all the potential speed a snowboarder has perched on the lip of the half pipe!
The Laws of Thermodynamics
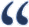 If your theory is against the second law of thermodynamics,
If your theory is against the second law of thermodynamics,
I can give you no hope.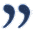

One morning, as you hop in the car to drive to school, you notice that the fuel gauge shows almost no gas left in the car, yet you shrug and assume you'll make it anyway. About halfway to school, you run out of gas completely. However, surprisingly, your car continues to function, driving nearly 10 more miles to get you to school!
Why can't this happen? What law of the universe is being violated?

Imagine making yourself a nice hot cup of cocoa and then…the phone rings. When you finish with the phone call, you take a sip and – OUCH! – the cocoa is even hotter than when you left it to answer the phone, but it's just been sitting on the kitchen counter for the past 10 minutes!
Can this happen? What law of the universe is being broken?
© KC Distance Learning. All rights reserved. Updated 2020-2021 by DVHS.
Matter: anything that has mass and volume.
Atom: The basic units of matter consisting of dense nuclei surrounded by clouds of negatively charged electrons.
Energy: The capacity to do work or transfer heat.