1342.12 Companion
July 12, 2017
Page 131
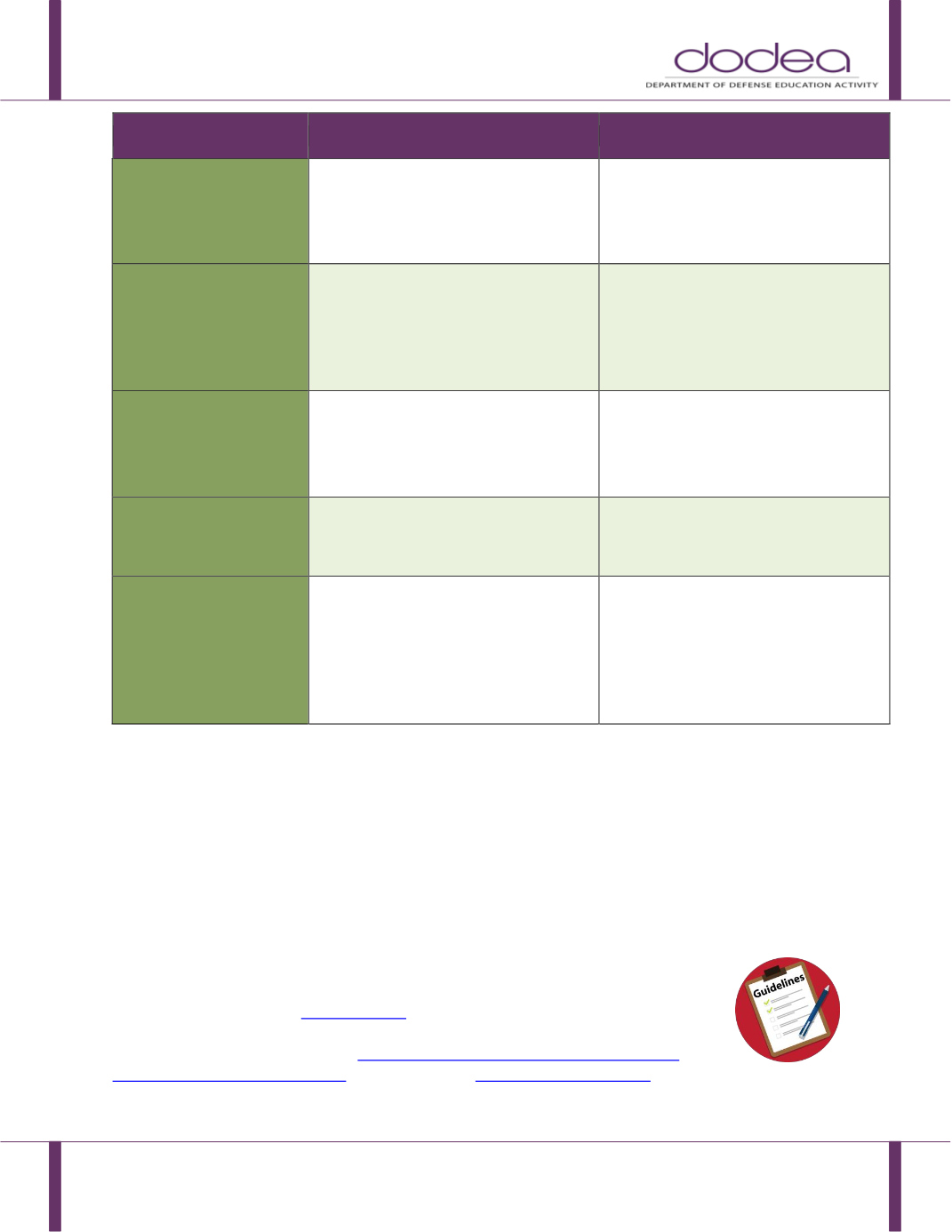
Characteristics
ELL Student WITHOUT a Disability
ELL Student WITH a Disability
different areas (such as oral and
writing skills)
English progress should continue
steadily even if slowly
• May show a marked discrepancy
between different areas (such as
oral and writing skills) which cannot
be attributed to lack of sufficient
time or appropriate interventions
HEALTH
No significant health characteristics.
History of ear infections, hearing
problems, sleep or eating
disturbances, incontinence, and
family incidence of learning
disability may have influence on
learning.
SENSORY
FUNCTIONING
May exhibit periodic “overload”
response such as gazing off and
blanking out what is heard for short
periods of time during an initial
adjustment to new setting
Auditory or visual processing
difficulties exhibited over period of
time without signs of improvement
MOTOR
SKILLS
Normal
Exhibits fine and/or gross motor
impairments.
PRODUCTIVITY
May have difficulty with verbal and
written directions or
beginning/switching tasks due to
insufficient English development
but often finds strategies or
techniques for coping
May have difficulty with verbal and
written directions or beginning/
switching tasks for a variety of
reasons and may not acquire
strategies for coping; has difficulty
completing tasks following explicit
instructions
Special Education Program Guidelines for English Language Learners
Under the DoDEA program, guidelines for special education and English Language Learners (ELLs) a
student receiving ESL services can be referred for and receive special education services while also being
served by the ESL teacher. The classroom teacher, parent, or any other individual who has relevant
knowledge about the student’s educational performance can make a referral for special education
evaluation.
Prior to the Case Study Committee (CSC) accepting a referral, the initial task of the ESL and general
education teacher(s) is to differentiate the student’s performance issues and length of time that the
student has been exposed to linguistic and cultural differences, limited environmental factors, lack of
instruction, or a suspected disability.
The specific guidelines that govern the referral and eligibility process for special
education are described i
n DoDM 1342.12Enclosure 4, S 2, 6, 7 p 24, 27, 30 “Provision
of Early Intervention and Special Education Services to Eligible DoD Dependents,” dated
June 17, 2015, and the English as
a Second Language Program Guide: Planning for English Language Learner Success ,March 2007 and
DoDEA regulation 2440.1 ,“English
as a Second Language Programs,” March 16, 2007.