The Economics of New Technology
The high demand for new technology moved the United States toward a modern capitalist economy. Employers needed workers and workers needed pay. Many employers used a wage labor system where the worker is under contract to the employee and is paid a predetermined wage for their labor. In some industries, employers paid workers by the number of items produced or weight of items produced as in agricultural industries. What are the pros and cons of each pay system? Who benefits?
 |
Corporate capitalism began to replace merchant capitalism by the mid-nineteen century. Merchants engaged in domestic and foreign trade. They used ships to make trips to Europe and bring goods to the United States. Their businesses grew as improvements in steam ships began to take the place of the more labor-intensive sailing ships. New inventions made manufacturing possible. Manufacturing was the process of taking raw goods and turning them into usable products. Merchants began to realize that manufacturing was more profitable than trade.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution, businesses were small and generally had one owner. Large factory operations with many workers needed capital, or money, to operate. Corporations formed and capital was raised by selling shares of the company to people who became shareholders or investors. This was called buying stock in the company. People who bought stock were buying a small piece of ownership of the company. When the company made a profit, people who owned shares were paid a dividend. The shares or company stock became worth more than what was originally paid to purchase them. The shareholders could sell their shares and take the profit or they could reinvest their profits into the company to finance growth and the research and development of new products.
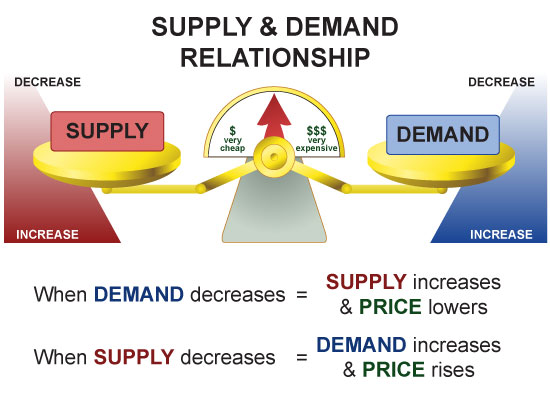
Corporations operated under the theory of a free market economic system whereby the business, not the government, decided what to produce and how to price it. Under a free market system, competition and supply and demand would control prices of goods and services.
 |
It was attractive for investors to put money into companies. The laws permitted shareholders to have limited liability. This meant that a shareholder only lost the money that they originally used to buy the stock. They were not liable for the greater company loss.
|
|
Innovations in technologies to improve daily life and technologies to increase the efficiency of manufacturing goods created jobs and new dreams of a bright future. The table was set for the increased growth of big business and a need for greater regulation.
