Consequences of Melting Sea Ice and Ice Caps
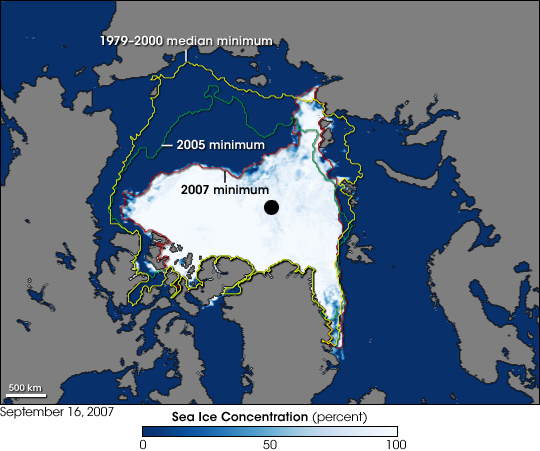
Global trends show that sea ice is shrinking and that the polar ice caps are melting as Earth becomes gradually warmer due to the enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming. Several consequences arise from this melting of the polar ice. This map shows how sea ice is shrinking in the Arctic region of the globe. The yellow line shows the outline of where the ice was prior to the year 2000. You can see that it has shrunken considerably just between 2000 and 2007.
Check out the items below to learn more about some of the consequences of melting sea ice.
Trend in Global Sea Level Rises
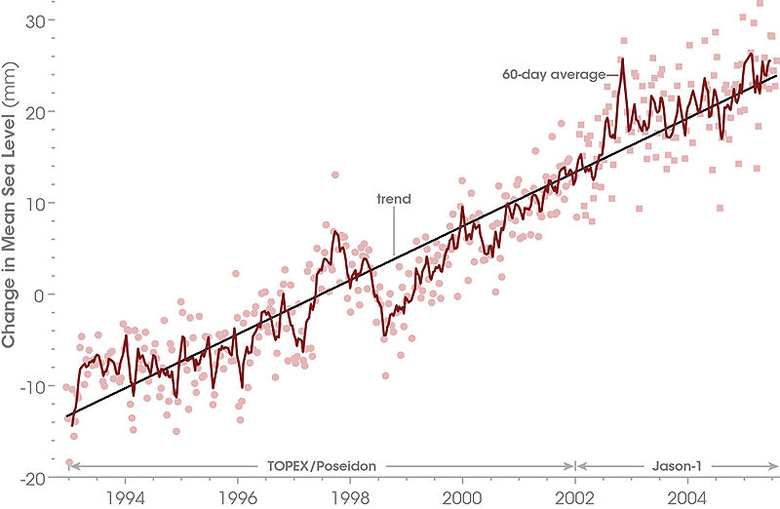
One of the most obvious consequences of global warming is shifted shorelines. As the oceans warm, the water undergoes thermal expansion and takes up more space, thus causing a rise in sea level. Sea level rises are being noted all over the globe. Rises in sea level will mean that coastal areas that are now dry land will gradually be placed under water. This further leads to more flooding, changes in ecosystems, and the displacement of human-populated cities.
Shrinkage of Polar Bear Habitat
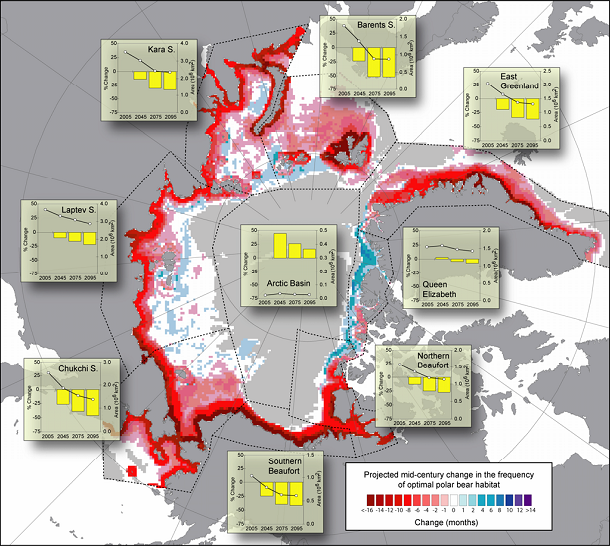
A direct consequence of polar ice melting is the loss of wildlife habitat. Many large mammals, like polar bears, walruses, and seals, rely on the polar ice as habitat and for hunting their food. As the polar ice retreats, these animals lose their vital habitat. They also must shift their feeding and migration routes. This map shows how polar bear habitat is expected to diminish over the next few decades if global warming continues. The darker red areas are those areas where habitat loss is the greatest. The native peoples who hunt these animals will also be affected. Native people of some Arctic cultures depend on hunting seals and walruses for food and other needs. As these animals’ migration paths and habitats are disrupted by melting ice, the lives of the people that hunt them will also be disrupted.
Methane Release

Melting of sea ice and the polar ice caps will also result in greater release of methane gas to the atmosphere. Arctic soils and ice hold large quantities of this gas. As the ice melts, the gas is released to the atmosphere. Methane, like carbon dioxide, is a greenhouse gas, and so release of it to the atmosphere would just accelerate global warming. This scientist is measuring methane release from an Arctic soil.