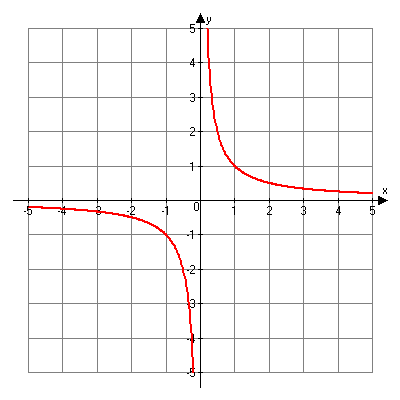
Transformations of Rational Functions
The parent function for rational equations is ![]() .
.
![]()
Just like with quadratic, square root, and cube root functions, changing the "a", "h", and "k" values in the general equation 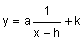 transforms the parent function
transforms the parent function ![]() .
.
|