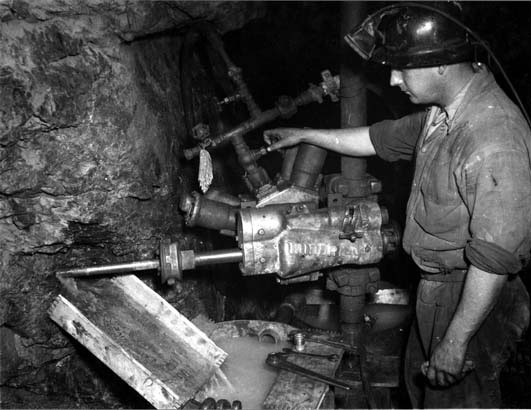
Subsurface Mining
When mineral ores are too deep to get at with the surface mining techniques, subsurface mining methods are used instead. An advantage of subsurface mining is that it disturbs much less land than surface mining. In fact, it disturbs less than one-tenth the amount of land as surface mining. Click each image to learn about some methods of subsurface mining.