Exponential Decay
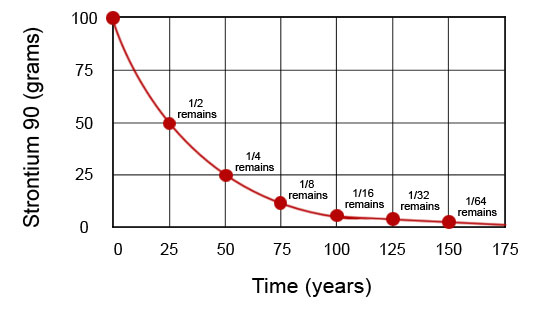
Refer back to the graph you completed for the warm-up activity of this section. Notice the curved nature of the line you plotted and compare it to the graph of the radioactive decay of strontium-90 atoms shown here.
All radioactive decay takes place such that a characteristic curved graph, like this, is produced. This type of decay is called exponential decay. It is in contrast to linear decay, which takes place when change is uniform, like sand moving through an hourglass. If half of the sand in an hourglass is gone in one hour, then all of it will be gone in two hours. Exponential decay is different. If half of a radioactive isotope decays in one hour, half of the remainder, or one-fourth, will be depleted in two hours, leaving one-fourth.