 Multiple Choice: Cross-Cutting Relations
Multiple Choice: Cross-Cutting Relations
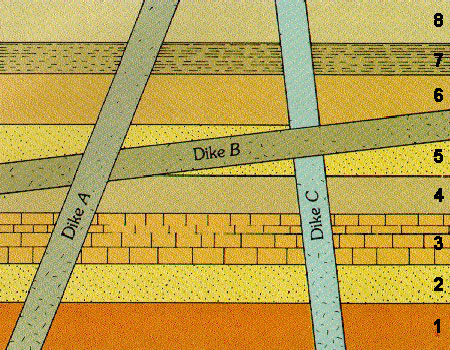
Here is a more difficult example of how cross-cutting relations can be used to assign relative ages to rock layers and events. Now that you have learned about some principles of relative dating, study the image and see if you can answer the questions that follow. You can use any principle of relative dating you have learned about so far.